- Have any questions?
- +91 9951606000
- sales@sriagasthyalifesciences.com
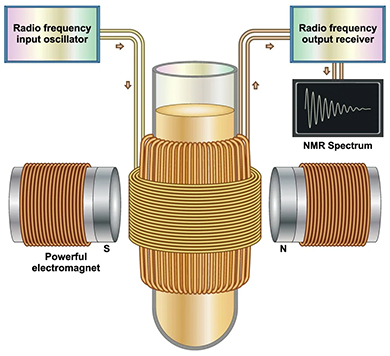
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to determine the molecular structure and chemical composition of a sample. It works by analyzing the interaction of spinning nuclei in a strong magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, a stationary external magnetic field causes certain nuclei in a molecule to absorb selective radiofrequencies. The energy absorbed induces a transition in nuclear spins, which is observed on an NMR spectrum.
APPLICATIONS OF NMR SPECTROSCOPY
NMR spectroscopy is a non-destructive and non-invasive technique that is used to determine molecular structure and dynamics. The applications of NMR are diverse and include the following research areas and industries:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Sri Agasthya Life Sciences, An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company trades high quality laboratory chemicals of Merck Life Science Pvt.Ltd.